Callback Signaling
The callback mechanism implies an event driven behavior. The following description uses the Surface Processing signal as an example of callback generating event.
The Surface Processing signal occurs when a transfer phase terminates. It is issued by a channel to indicate that the destination memory surface has been filled with an image coming from the source camera, and that this surface is available for image processing (see SurfaceState).
The image processing task is performed on this event by a special function called the callback function.
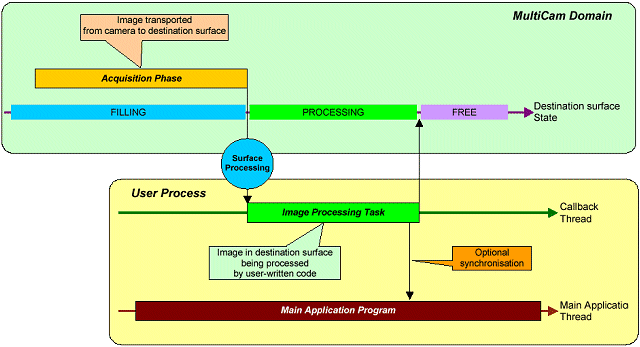
Callback mechanism
The callback function is called by the MultiCam driver, not by the user application. This ensures that the image-processing task is realized at the ideal instant, exactly when the surface becomes ready for processing.
MultiCam benefits from several built-in features to ease the implementation of the callback function.
| ● | A dedicated thread is created for the callback function execution. |
| ● | The callback function prototype is declared in the MultiCam system C header file. |
| ● | Means are provided to designate the channel and the signal(s) issuing the callback function calls. |
| ● | The callback function argument provides all relevant information to the user-written code. |
The MultiCam function to register a callback function to a channel or a processor is McRegisterCallback.
Callback Function Prototype
The callback function prototype is declared in the MultiCam system's MultiCam.h header file as follows:
typedef void (MCAPI *PMCCALLBACK)(PMCSIGNALINFO SignalInfo);
|
Item |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Function |
PMCCALLBACK |
Callback function |
|
SignalInfo |
PMCSIGNALINFO |
Argument providing the signal information structure. |
The user should define the callback function in the application code in accordance with this prototype.
The callback function is called by the MultiCam driver when a channel or a processor issues a pre-defined signal.
The pre-defined signal should be enabled with the SignalEnable parameter. It is allowed to enable several signals.
If more than one enabled signals are issued simultaneously from an object, the callback function is successively called for each signal occurrence.
When the signal occurs, the callback dedicated thread is released, and the callback function is automatically invoked. The thread is restored to an idle condition when the callback function is exited.
The function has a single argument, which is a structure passing information on the signal that caused the callback function. This structure has the signal information type.
If the callback signaling mechanism is used, the waiting and advanced signaling mechanisms cannot be used.
Registration of Callback Function
A callback function should be registered to a channel or processor object before use. Only one callback function per object is supported.
Registering the callback function results into the creation in the application process of a separate thread dedicated to the callback function. This thread is maintained in a idle state until a signal occurs. There can be only one dedicated thread per channel or processor object.
A dedicated MultiCam function is provided for callback registration: McRegisterCallback.
Context
Context is an argument of the callback registration function as well as a member of the signal information structure available to the callback function.
The user is free to use this item at the registration time to hold any identifying information he may find useful.
When the callback function is executed, the user gets back the context information as it was passed to the registration function.
The following code uses the callback mechanism to process images grabbed during an acquisition sequence. One or several surfaces have to be created and assigned to the cluster owned by the channel. At the end of each acquisition phase, the surface is filled and made available to the callback function. The Status variable can be used for error checking.
[C]
void MyApplication()
{
//Application level initializing code
MCSTATUS Status = McOpenDriver(NULL);
//Application level initializing code
MCHANDLE MyChannel;
Status = McCreateNm("EXPERT_A", &MyChannel);
//Assign grabber and camera to channel
//Configure channel including triggering mode
//Assign to channel a destination cluster of surfaces
//Registering the callback function
Status = McRegisterCallback(MyChannel, MyFunction, NULL);
//Activating acquisition sequence
Status = McSetParamInt(MyChannel, MC_ChannelState, MC_ChannelState_ACTIVE);
//Acquisition sequence is now active
//A callback is automatically generated after each acquisition phase
//Deleting the channels
Status = McDelete(MyChannel);
//Disconnecting from driver
Status = McCloseDriver();
}
void MCAPI MyFunction(PMCSIGNALINFO SignalInfo)
{
//...
//Image processing code
//Image to be processed is available in the destination cluster of surfaces
//...
}
