Non-Linear Filtering
These functions use non-linear combinations of neighboring pixels to highlight a shape, or to remove noise.
Most can be destructive (except top-hat and median filters) i.e. the source image is overwritten by the destination image. Destructive operations are faster.
All have a gray image and a bilevel equivalent, for example ErodeBox and BiLevelErodeBox.
- They define the required shape by a Kernel (usually in a 3x3 matrix).
- They slide this Kernel over the image to determine the value of the destination pixel when a match is found:
- Erosion, Dilation: shrinks / grows image regions.
- Opening, Closing: removes / fills image region boundary pixels.
- Thinning, Thickening: erodes / dilates using image pattern matching.
- Top-Hat filters: retains all the tiny image details while removing everything else.
- Morphological distance: indicates how many erosions are required to make a pixel black.
- Morphological gradient: indicates the outer and inner edges of the erosion and dilation processes.
- Median filter: removes impulsive noise.
- Hit-and-Miss transform: detects patterns of foreground /background pixels, can create skeletons.
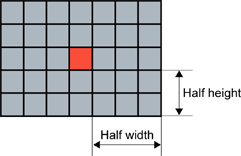
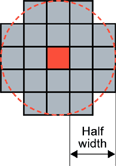
Rectangular kernel of half width = 3 and half height = 2 (left) Circular kernel of half width = 2 (right)
The morphological operators combine the pixel values in a neighborhood of given shape (square, rectangular or circular) and replace the central pixel of the neighborhood by the result.
Three special cases are most often used erosion, dilation and median filter where : K can be 1 (minimum of the set), N (maximum) or N/2 (median).
Erosion, Dilation, Opening, Closing, Top-Hat and Morphological Gradient operations all use rectangular or circular kernels of odd size. Kernel size has an important impact on the result.
examples
|
HalfWidth/HalfHeight |
Actual width/height |
|---|---|
|
0 |
1 |
|
1 |
3 |
|
2 |
5 |
|
3 |
7 |
Erosion reduces white objects and enlarges black objects, Dilation does the opposite.

|

|
| Erosion | Dilation |
Erosion thins white objects by removing a layer of pixels along the objects edges: ErodeBox, ErodeDisk. As the kernel size increases, white objects disappear and black ones get fatter.
Dilation thickens white objects by adding a layer of pixels along the objects edges: DilateBox, DilateDisk. As the kernel size increases, white objects get fatter and black ones disappear.
Opening removes tiny white objects / dust. Closing removes tiny black holes / dust.
|

|
| Opening | Closing |
An Opening is an erosion followed by a dilation using OpenBox, OpenDisk.
The global effect is to preserve the overall shape of objects, while removing white details that are smaller than the kernel size.
A Closing is a dilation followed by an erosion using CloseBox, CloseDisk.
The global effect is to preserve the overall shape of objects, while removing the black details that are smaller than the kernel size.
These functions use a 3x3 kernel to grow (Thick) or remove (Thin) pixels:
- Thinning: can help edge detectors by reducing lines to single pixel thickness.
- Thickening: can help determine approximate shape, or skeleton.
When a match is found between the kernel coefficients and the neighborhood of a pixel, the pixel value is set to 255 if thickening, or 0 if thinning. The kernel coefficients are:
- 0: matching black pixel, value 0
- 1: matching non black pixel, value > 0
- -1: don't care
Top-hat filters are excellent for improving non-uniform illumination.


White top-hat filter: source and destination images
They take the difference between an image and its opening (or closure). Thus, they keep the features that an opening (or closing) would erase. The result is a perfectly flat background where only black or white features smaller than the kernel size appear.
- White top-hat filter enhances thin white features: WhiteTopHatBox ,WhiteTopHatDisk.
- Black top-hat filter enhances thin black features:BlackTopHatBoxBlackTopHatDisk.
Distance computes the morphological distance (number of erosion passes to set a pixel to black) of a binary image (0 for black, non 0 for white) and creates a destination image, where each pixel contains the morphological distance of the corresponding pixel in the source image.
The morphological gradient performs edge detection - it removes everything in the image but the edges.
The morphological gradient is the difference between the dilation and the erosion of the image, using the same structuring element.
MorphoGradientBox, MorphoGradientDisk.

Dilation – Erosion = Gradient
The Median filter removes impulse noise, whilst preserving edges and image sharpness.
It replaces every pixel by the median (central value) of its neighbors in a 3x3 square kernel, thus, outer pixels are discarded.


Median filter: source and destination images
Hit-and-miss transform operates on BW8, BW16 or C24 images or ROIs to detect a particular pattern of foreground and background pixels in an image.
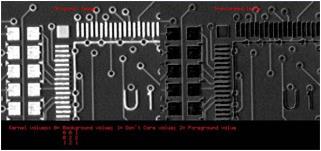
Hit-and-miss transform
The HitAndMiss function has three arguments:
- A pointer to the source image of type EROIBW8, EROIBW16, or EROIC24
- A pointer to the destination image of type corresponding to the type of the source image.
The sizes of the source and destination images must be identical. - A kernel of type EHitAndMissKernel Two constructors are available for the kernel object:
- EHitAndMissKernel(int startX, int startY, int endX, int endY) where:
startX, startY are coordinates of the top left of the kernel, must be less than or equal to zero.
endX, endY are coordinates of the bottom right of the kernel, must be greater than or equal to zero.
The constructed kernel has no explicit restrictions on its size, and the following characteristics:
kernel width = (endX – startX + 1), kernel height = (endY – startY + 1) - EHitAndMissKernel(unsigned int halfSizeX, unsigned int halfSizeY) where:
halfSizeX is half of the kernel width – 1, must be greater than zero.
halfSizeY is half of the kernel height – 1, must be greater than zero.
The constructed kernel has the following characteristics:
kernel width = ((2 x halfSizeX) + 1), kernel height = ((2 x halfSizeY) + 1)
kernel StartX = - halfSizeX, kernel StartY = - halfSizeY
- EHitAndMissKernel(int startX, int startY, int endX, int endY) where:
The hit-and-miss transform can be used to locate corners.

Binary source image
1. Define the kernel by detecting the left corner. The left corner pixel has black pixels on its immediate left, top and bottom; and it has white pixels on its right. The following hit-and-miss kernel will detect the left corner:
- +
- + +
- +
2. Apply the filter on the source image. Note that the resulting image should be properly sized.

Resulting image, highlighted pixel is located on left corner of rhombus
3. Locate the three remaining corners in the same way: Declare three kernels that are the rotation of the filter above and apply them.
4. Detect the right, top and bottom corners.



