Calibration and Transformation
Field-of-view calibration
|
Calibration establishes the relationship between real-world point coordinates and image pixels. A simple calibration model computes faster, a repeatable part position is easier to locate.
|
|
The Raw sensor coordinate system starts from upper left and extends rightwards and downwards.
The range of abscissas is 0 to width-1 and the range of ordinates is 0 to height-1 where integer coordinate values correspond to pixel centers. |
|
| The Centered sensor coordinate system starts at the center ([width-1]/2, [height-1]/2 in the Raw system) and extends rightwards and upwards. |
|
|
The real world 3D coordinates are defined in a 2D reference frame tied to a reference plane. The origin and direction of the axis are normally aligned with major features of the inspected parts.
|
|
Before World-to-Sensor Transform
Before converting from world to sensor coordinates, sources of distortion should be eliminated:
|
□
|
adjust sweep frequency or scanning speed to avoid non-square pixels. |
|
□
|
adjust optical alignment to minimize perspective effect. The field of view should be parallel to the sensor plane. |
|
□
|
use long focal distances and good quality lenses to minimize Optical distortion. |
|
□
|
use appropriate scale factor based on lens magnification, observation distance and focusing. |
|
□
|
minimize skew and translation effects by secure fixtures, and part-movement / acquisition-triggering synchronization. |
Effects of World-to-Sensor Transform
|
●
|
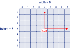
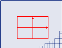
No calibration. World and sensor coordinates are identical. |
|
|
|
●
|
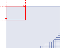
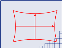
Translated calibration: The coordinate origin can be moved. World coordinates correspond to pixel units. |
|
|
|
●
|
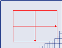
Isotropic scaling (square pixels). A scale factor converts pixel values to physical measurements. |
|
|
|
●
|
Anisotropic scaling (non-square pixels). Uses two scale factors with pixel aspect ratio (X /Y ) in the range [-4/3, -3/4] (or [3/4, 4/3]). Pixels are always displayed as square, so the image appears stretched. |
|
|
|
●
|
Scaled and skewed (square pixels). Real-world axis aligns with rotated inspected part using translation, rotation and scaling. |
|
|
|
●
|
Scaled and skewed (non-square pixels). Distortion is apparent. Occurs when camera scan speed does not match pixel spacing. |
|
|
|
●
|
Perspective distortion causes further away objects to look smaller; lines remain straight but angles are not preserved. |
|
|
|
●
|
Optical distortion causes cushion or barrel appearance of rectangles. |
|
|
|
●
|
Combined distortions result in a complex, non linear, transform from real-world to sensor spaces. |
|
|