QR Codes Specifications
QR code definition
A QR code is a square array of dark and light dots. One dot (or "module") represents one bit of information.
QR codes contain various types of data and can be different models, versions, and levels. They always contain a message, metadata about alignment, size, format, and error correction bits. They comply with the international standard ISO/IEC 18004 (1, 2 and 2005).
QR code structure
The QR code symbol consists of an encoding region, containing data and error correction codewords, and of function patterns, containing symbol metadata and position data.
A QR code must be structured with the following elements:
| □ | Quiet zone: blank margin around the QR code |
| □ | Finder patterns: recognizable zones identifying a QR code |
| □ | Extension patterns: markers for the alignment of the QR code (model 1) |
| □ | Alignment patterns: markers for the alignment of the QR code (models 2 and 2005) |
| □ | Timing Patterns: data giving the module size (in pixels) |
| □ | Format information: zones providing the QR code level |
| □ | Version information: data giving the QR code size, for instance 25 x 25 modules (models 2 and 2005) |
| □ | Data contents and error correction codewords: the primary information carried by the symbol, with additional information for error correction |
Variants of this structure exist, according to the model, format, or version of the QR code. For instance, model 1 QR codes do not feature Geometrical property of a coded element. alignment patterns but extension patterns. Micro QR codes include only one finder pattern, and no alignment pattern.
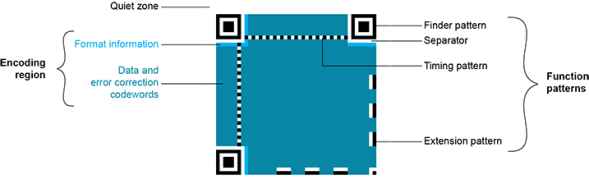
Structure of a model 1 QR code symbol
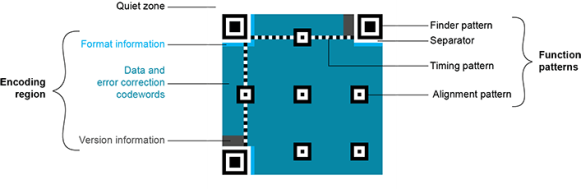
Structure of a QR code 2005 symbol
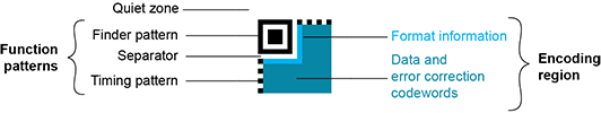
Structure of a Micro QR code symbol
QR code subtypes
A QR code can be one of the following subtypes:
| □ | Basic: the default subtype. |
| □ | ECI (Extended Channel Interpretation): the ECI subtype provides a consistent method to embed interpretation information of data in the QR code. The ECI protocol is defined in the AIM Inc. International Technical Specification. (ECI is not available for Micro QR code symbols.) |
| □ | GS1: the data contained in the QR code are formatted in accordance with the GS1 General Specification. |
| □ | AIM: the data contained in the QR code are formatted in accordance with a specific industry application previously agreed with AIM Inc. The application indicator value is embedded in the QR code data. |
Data types
The QR code data can be any mix of these types:
| □ | Numeric data (0-9) |
| □ | Alphanumeric data (0-9, A-Z, /,$ , %...) |
| □ | Byte data (possibly ECI-encoded) |
| □ | Kanji characters |
Byte data interpretation
In a QR code, the byte data can represent any information. Their interpretation depends on the subtype of the QR code:
| ● | Basic subtype: |
| □ | If some byte data are present in the QR code, you need to know how to interpret them. |
| □ | Use the EByteInterpretationMode enum to select the corresponding byte interpretation mode (see the retrieving decoded data section in Reading QR Codes for more details). |