The Bayer filter is a special color image encoding format that allows to capture color information from a single sensor.
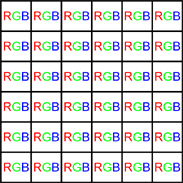
True color pattern
To capture color information with only one sensor, a color filter with a specific layout is placed in front of the sensor, so that part of the pixels receive green light only, while others receive red or blue only.
50 % of the total number of pixels are green, 25 % are red, 25 % are blue. (More pixels are dedicated to green than to red and blue, because the human eye is more sensitive to that color.)
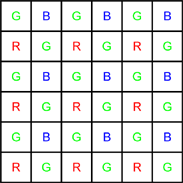
Bayer pattern
An image encoded after the Bayer pattern has the same format as a gray-level image, and conveys three times less color data. The true horizontal and vertical resolutions are smaller than those of a true color image.
To supply missing component values and obtain a full-color image, various algorithms can be used. The complete red, green, and blue values for each point can be interpolated by mere duplication (nearest neighbor technique) or by linear interpolation.
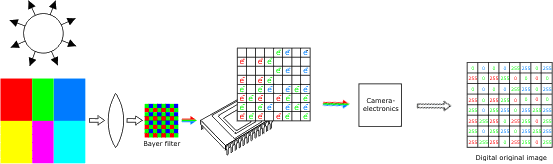
Digitizing an image with a Bayer filter
