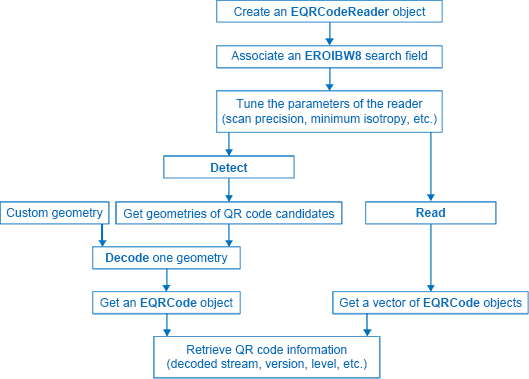
EasyQRCode detects QR (Quick Response) codes in an image, decodes them, and returns their data.
Error detection and correction algorithms ensure that poorly-printed or distorted QR codes can still be read correctly.
A QR code is a square array of dark and light dots. One dot (or "module") represents one bit of information.
QR codes contain various types of data and can be different models, versions, and levels. They always contain a message, metadata about alignment, size, format, and error correction bits. They comply with the international standard ISO/IEC 18004 (1, 2 and 2005).
The QR code symbol consists of an encoding region, containing data and error correction codewords, and of function patterns, containing symbol metadata and position data.
A QR code must be structured with the following elements:
- Quiet zone: blank margin around the QR code
- Finder patterns: recognizable zones identifying a QR code
- Extension patterns: markers for the alignment of the QR code (model 1)
- Alignment patterns: markers for the alignment of the QR code (models 2 and 2005)
- Timing Patterns: data giving the module size (in pixels)
- Format information: zones providing the QR code level
- Version information: data giving the QR code size, for instance 25 x 25 modules (models 2 and 2005)
- Data contents and error correction codewords: the primary information carried by the symbol, with additional information for error correction
Variants of this structure exist, according to the model, format, or version of the QR code. For instance, model 1 QR codes do not feature alignment patterns but extension patterns. Micro QR codes include only one finder pattern, and no alignment pattern. EasyQRCode can read all of them.
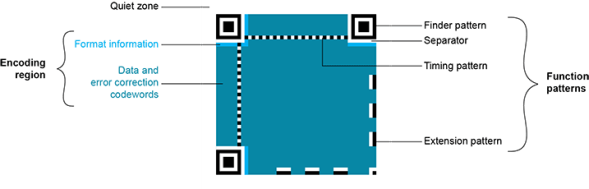
Structure of a model 1 QR code symbol
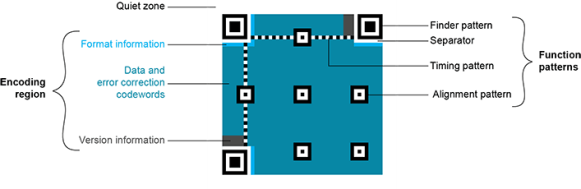
Structure of a QR code 2005 symbol
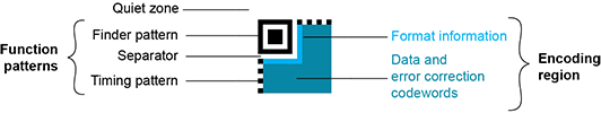
Structure of a Micro QR code symbol
The QR code data can be any mix of these types:
- Numeric data (0-9)
- Alphanumeric data (0-9, A-Z, /, $, %, etc.)
- Byte data
- Kanji characters
- Model 1: original QR code international standard, with versions ranging from 1 to 14.
Note that the "version" of a QR code is the symbol size (in number of modules). It does not relate to the version of the standard, which is called the "model". - Model 2: improvement of model 1. It provides versions from 1 to 40. It defines alignment patterns to improve reading of distorted QR codes, or QR codes printed on curved surfaces.
- Model 2005: improvement of model 2, including white-on-black QR codes, and mirror symbol orientation.
- Micro QR codes: (not yet supported) smaller QR codes, from version M1 to version M4. They have been introduced to save printing space.
- QR codes: from version 1 (21 x 21 modules) to version 40 (177 x 177 modules), with an increment of +4 x +4 modules (version 2: 25 x 25 modules, version 3: 29 x 29 modules, ..., version 39: 173 x 173 modules).
- Micro QR codes: (not yet supported) version M1 (11 x 11 modules), version M2 (13 x 13 modules), version M3 (15 x 15 modules), version M4 (17 x 17 modules).



Examples of QR codes
From left to right:
Micro QR code, version M3, 15 x 15 modules,
Model 2 QR code, version 4, 33 x 33 modules, 67-114 characters,
Model 2 QR code, version 40, 177 x 177 modules, 1852-4296 characters
QR codes contain error correction data. The standard offers the following levels of error correction:
- L: (low) about 7% of codewords can be restored
- M: (medium) 15%
- Q: (quality) 25%
- H: (high) 30% (not available for Micro QR codes)
When the QR code reader finds an array of dots that could match a QR code, it returns the "geometry" of this QR code candidate.
A QR code geometry is a set of points. It contains the coordinates of the corners of the QR code quadrilateral (bottom left, top left, top right, bottom right), and the coordinates of the finder pattern centers (bottom left, top left, top right).
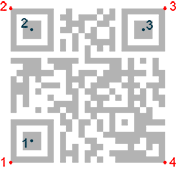
QR code geometry
- Set a search field on an EROIBW8 image or tune the parameters to restrict the numbers of operations to process.
- The QR code reader scans the image and searches for 3 finder patterns that could match a QR code, with the following requirements:
- Minimum quiet zone (blank zone around the QR code) width: 3 pixels.
- Minimum module size: 3 x 3 pixels.
- Minimum isotropy: 0.5.
- Maximum corner deformation: 15° (corner angles can range from 75° to 105°).
- The reader returns QR code candidates, or the result of a detection, as a vector of geometries.
-
The QR code reader decodes a QR candidate and returns the QR code: model, version, level, geometry and decoded stream of data.
The decoded stream class consists of a coding mode (basic, FNC1/GS1, or FNC1/AIM), and an application indicator (if the coding mode is FNC1/AIM, otherwise 0). The decoded data can be accessed from each part of the decoded stream, according to its encoding (numeric, alphanumeric, byte, or Kanji). You can also get the raw bit stream (the bit data after unmasking and error correction, but before decoding as a vector of bytes).
- The reader can report the amount of unused error correction.
- Close to 1, very few errors were corrected when decoding the data. The decoding is highly reliable, and the QR code is of good quality.
- Close to 0, many errors were corrected when decoding the data. The decoding is reliable, but the QR code quality is poor.
- -1, error correction failed. Decoding was not performed.
Scan precision: You can change the scan precision to scan the search field with a fine (recommended for small QR codes), or coarse (recommended on medium to large QR codes) precision.
Minimum score: The QR code reader searches for this QR code finder pattern: 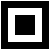
A perfect match returns a pattern finder score of 1.
Less accurate matches return lower scores.
The minimum score allowed by default is 0.65 - you can tune this.
Minimum isotropy: The isotropy of a QR code represents its rectangular deformation.
Perfectly square QR codes have an isotropy of 1 (short side divided by long side, whether the rectangle is vertical or horizontal).
EasyQRCode can detect rectangle QR codes with an isotropy down to 0.5. The default minimum isotropy is 0.8, it can be tuned from 0 to 1.



Square and rectangular QR codes (isotropy = 1, 0.5, and 0.5 from left to right)
Model and version: The QR code reader searches for QR codes of all models, and all versions.
You can shorten the process by specifying the QR code model(s) and a range of versions (from 1 to 40) to be searched for.