Surface Allocation Rules
This section summarizes all the rules applicable to the allocation of MultiCam surfaces in the host PC memory for Grablink Base, Grablink DualBase, and Grablink Full exclusively.
The MultiCam driver exhibits the following limitations concerning the number of surfaces:
| ● | The maximum number of surfaces instantiated within an application is 4096. |
| ● | The maximum number of surfaces assigned to a channel is 4096. |
| ● | The maximum number of surfaces per board is 4096. |
Dynamic DMA
Note: On
The Windows operating systems exhibit the following limitations for the maximum buffer size allowed per MultiCam surface:
| ● | About 64 Megabytes under Windows XP x86; |
| ● | About 32 Megabytes under Windows XP x64; |
| ● | About 2 Gigabytes under Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008; |
| ● | About 4 Gigabytes under Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2. |
Note: If a MultiCam surface exceeds those limits, MultiCam returns MC_IO_ERROR at channel activation.
Applies to:
These Grablink boards implement "dynamic DMA" meaning that, if required, the descriptors lists are stored in the host PC memory.
When this happens, prior to the transfer of any surface into the host PC memory, the MultiCam driver copies the corresponding descriptors list into the on-board memory reserved for that purpose.
The "dynamic DMA" feature relaxes the constraints about the total amount of descriptors for all the surfaces belonging to the channel. However, the descriptors of one surface must fit within the on-board being board dependent. Consequently, the rule becomes:
| ● | For |
| ● | For each channel of |
| ● | For |
The number of descriptors required for a surface is depending on multiple factors:
| ● | The fragmentation of the memory allocated by the operating systems; usually, the memory is allocated by non-contiguous blocks of 4096 bytes forcing a new descriptor for every block boundary. |
| ● | The alignment of the MultiCam surface on the memory blocks. |
| ● | The usage of the ImageFlipY function requires a descriptor boundary at each line boundary. |
| ● | The usage of RGB planar formats requires a descriptor boundary at each line boundary for each color component. |
A practical, but very conservative, rule to estimate the number of descriptors for a surface is:

with BlockSize = 4096 Bytes.
Note: The rule used to decide to enable "dynamic DMA" is based on the above formulae. If the descriptors for all surfaces cannot fit in the on-board memory, the dynamic DMA is activated.
Applies to:
These Grablink boards activates the "Cropping in Hardware" feature to avoid descriptor boundaries at line boundaries when following conditions are met:
| ● | Monochrome or packed RGB image formats |
| ● | ImageFlipY is OFF |
When "Cropping in Hardware" is active, the following rule is applicable:
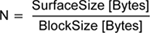
Note: "Cropping in Hardware" is particularly useful for small line sizes. The following diagram shows the maximum SurfaceSize vs. LineSize for a channel having a capacity of 2,000,000 descriptors (Grablink Base or Grablink DualBase).
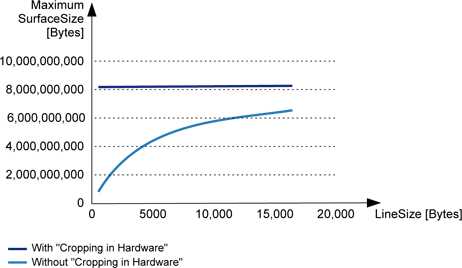
Maximum SurfaceSize vs. LineSize
Note: This rule is often less restrictive than the OS rule.
