Photometric Stereo and Process
Introduction
The Photometric Stereo is a technique used to estimate the normals at the surface of an object In a general content, the term object should be understood with the meaning of a class instance. In EasyObject, an object is a maximally-sized area of adjacent connected pixels belonging to the layer foreground..
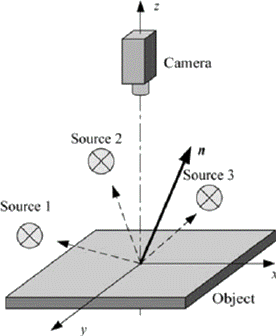
Photometric stereo setup
Source:
| ● | It takes at least 3 images of the same object taken under different known light directions. |
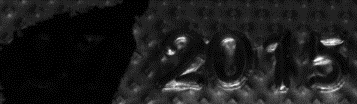
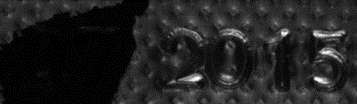
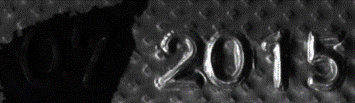
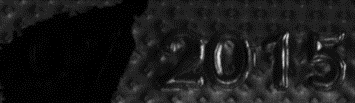
Inputs: images with different light directions
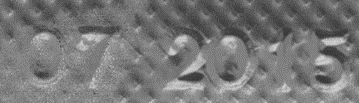
| ● | It produces an image containing the fraction of light reflected (called albedo) and the normal of the surface at each pixel. |


Outputs: albedos - normals
| ● | The normals are processed to compute gradients and curvatures, allowing to easily see bumps and holes. You can also integrate the normals to compute the height map. |

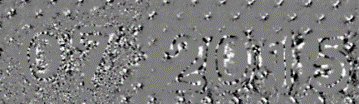
Outputs: gradients X - gradients Y - Gaussian curvatures
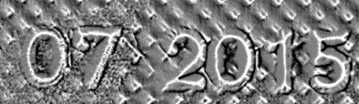

Outputs: mean curvatures - height map
Process
You can use the object Easy3D::PhotometricStereoImager in a 4-step process:
| 1. | Calibrate the setup from a sphere or from predefined angles (once per setup). |
| 2. | Perform the photometric stereo computation on the object images. |
| 3. | Retrieve the results. |
| 4. | Use and apply the Open eVision tools on the results. |
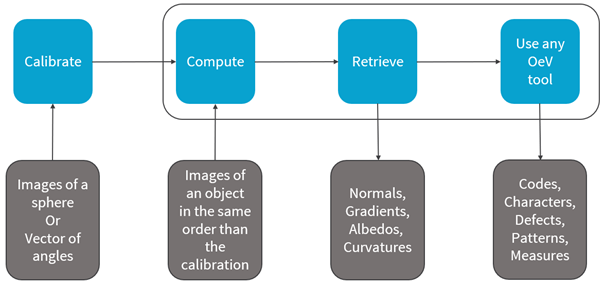
Photometric stereo process
Resources
| ● | The example described here demonstrates how to perform photometric stereo with Open eVision 3D libraries and tools. |
| ● | A sample application is also distributed with the source code. You can find it in …\Sample Programs\MsVc samples\3D Processing\Easy3DPhotometricStereo. |
| ● | This example and the sample application are based on the following resources: |
| □ | Open eVision 2.15 |
| □ | Microsoft Visual Studio 2017 |
The license for Easy3D is necessary to use the photometric stereo tools.